Health Informatics ETL Pipeline Project
This website showcases the development of our ETL pipeline.
Project maintained by SaiSrilekhaaluru Hosted on GitHub Pages — Theme by mattgraham
ETL Pipeline
| Home | |
| BPMN Model | |
| Use Case Model | |
| ETL Pipeline | |
| Insights | |
| Team Contributions | |
| About |
Introduction
In modern healthcare systems, data interoperability and seamless data exchange are critical for enhancing patient care, ensuring accurate diagnoses, and enabling effective decision-making. An Extract, Transform, Load (ETL) pipeline is an essential part of this process, ensuring that data is collected, processed, and integrated across various systems.
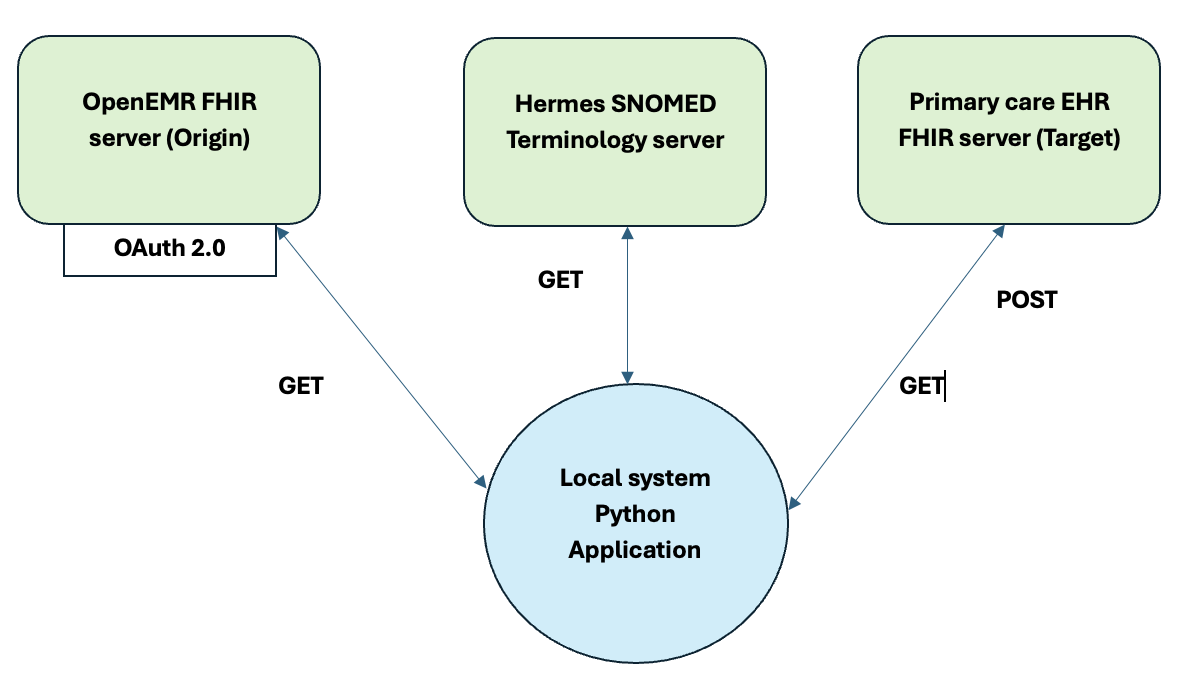
This ETL pipeline involves extracting healthcare data from different sources, transforming it into a consistent format, and then loading it into a target system to support clinical decisions and reporting. The pipeline in this context is designed to integrate data from the OpenEMR FHIR server (source) with the Primary Care EHR FHIR server (target). It leverages the Hermes SNOMED Terminology server for medical terminology standardization, and uses a Python application for the transformation process.
The steps of the pipeline are as follows:
Extraction: Data is fetched from the OpenEMR FHIR server using OAuth 2.0 authentication and a GET request. This data may include patient information, medical procedures, and diagnoses.
Transformation: The extracted data is processed by a Python application that standardizes, cleans, and formats it according to the needs of the target system. This includes mapping the data to SNOMED terminology standards via the Hermes SNOMED Terminology server.
Loading: After the data is transformed into the desired format, it is loaded into the Primary Care EHR FHIR server using a POST request. This process ensures that the data is available for clinical use and other healthcare operations.
The ETL pipeline is a powerful solution for ensuring that healthcare data from various systems is harmonized and can be used effectively across clinical workflows. This pipeline improves data accuracy, facilitates reporting, and ensures that patient information is processed in a compliant and efficient manner.
Task 1 - Parent Condition: Extraction, Transformation, and Loading Data onto the Target API
Overview of the Loading Process: In this task, the goal is to interact with the OpenEMR FHIR server, retrieve a patient’s conditions, extract the SNOMED concept ID of a condition, identify the parent term for that SNOMED concept, and create a Condition resource for the patient using the parent concept. This will be done by interacting with the Primary Care EHR FHIR server, specifically using the /Condition endpoint to load the new resource.
EXTRACTION:
Extract patient conditions from the OpenEMR FHIR server and retrieve the SNOMED concept ID of a specific condition for a given patient. Identify the parent SNOMED concept for the condition.
API Endpoint Details: OpenEMR FHIR Server:
OpenEMR(Source API): “https://in-info-web20.luddy.indianapolis.iu.edu/apis/default/fhir”
Primary Care EHR(Target API) “http://137.184.71.65:8080/fhir”
Authentication/Authorization Process:
Authentication: OAuth 2.0 authentication process, where an access_token is required to authorize API requests.
Authorization: Authorization token is retrieved from access_token.json and passed as a Bearer token in the request header.In order to refresh the token there is refresh_token.py
Error handling : While working on this task we need to access the access token which will expire after 1 hr so we need refresh the access token again and have to authorize it . Initially we faced a difficulty in understanding the process later some how we managed to do the process.
Get Access Token:
The function get_access_token_from_file() extracts the access token from the access_token.json file to authenticate API requests.
def get_access_token_from_file():
file_path = Path(data_dir / "access_token.json")
if not file_path.exists():
print("Error: access_token.json file not found.")
return None
try:
with open(file_path, 'r') as json_file:
json_data = json.load(json_file)
access_token = json_data.get("access_token")
return access_token
except (json.JSONDecodeError, KeyError) as e:
print(f"Error reading access token from file: {e}")
return None
Get Patient Resource ID:
The function get_patient_resource_id() extracts the patient resource ID from the patient_resource_id.txt file. python
def get_fhir_patient(resource_id):
url = f'{BASE_URL}/Patient/{resource_id}' # Extract data from FHIR server
response = requests.get(url=url, headers=get_headers())
data = response.json()
# Extract patient details from the response
birth_date = data.get('birthDate')
family_name = data['name'][0]['family']
given_name = data['name'][0]['given'][0]
address = data.get('address', [{}])[0]
line = address.get('line', [''])[0]
city = address.get('city', '')
district = address.get('district', 'N/A')
state = address.get('state', '')
postal_code = address.get('postalCode', '')
text = f'{line}, {city}, {state}, {postal_code}'
unique_patient_id = random.randint(10000, 99999)
gender = data.get('gender')
# Continue to use the extracted data for transformation
Extract Condition Data:
The function search_condition(patient_resource_id) is responsible for extracting condition data for a specific patient. The FHIR server is queried for conditions related to the given patient.
def search_condition(patient_resource_id):
url = f'{BASE_URL}/Condition?patient={patient_resource_id}' # Extract condition data
response = requests.get(url=url, headers=get_headers())
data = response.json()
if 'entry' in data:
conditions = data['entry']
first_condition = conditions[0]
snomed_code_from_openemr = first_condition["resource"]["code"]["coding"][0]["code"]
TRANSFORMATION:
The Transformation step involves processing or modifying the extracted data to fit the format required by the target system. Here, patient and condition data are mapped to predefined templates.
Transform Patient Data: The extracted patient data is mapped to the patient_template_dict to match the required FHIR structure.
Tools Used: FHIR Templates: Predefined JSON templates are used to ensure compliance with the FHIR standards for the Condition resource.
Python’s JSON Library: Python’s json module is used to parse and manipulate the data.
Requests Library: Used for interacting with the APIs
def get_fhir_patient(resource_id):
# Extract patient data (same as Extraction step)
...
# Transform patient data into template format
patient_template_dict["birthDate"] = birth_date
patient_template_dict['name'][0]['family'] = family_name
patient_template_dict['name'][0]['given'][0] = given_name
patient_template_dict['address'][0]['line'][0] = line
patient_template_dict['address'][0]['city'] = city
patient_template_dict['address'][0]['district'] = district
patient_template_dict['address'][0]['state'] = state
patient_template_dict['address'][0]['postalCode'] = postal_code
patient_template_dict['identifier'][0]['value'] = unique_patient_id
patient_template_dict['gender'] = gender
patient_template_dict['address'][0]['text'] = text
Transform Condition Data: The extracted condition data is mapped to the condition_template_dict to match the required FHIR structure.
def search_condition(patient_resource_id):
# Extract condition data (same as Extraction step)
...
# Transform condition data into template format
condition_template_dict["code"]["text"] = parent_concept_term
condition_template_dict["code"]["coding"][0]["display"] = parent_concept_term
condition_template_dict["code"]["coding"][0]["code"] = parent_concept_id
condition_template_dict['verificationStatus']['coding'][0]['code'] = first_condition['resource']['verificationStatus']['coding'][0]['code']
condition_template_dict["severity"]["coding"][0]["system"] = "http://snomed.info/sct"
condition_template_dict["severity"]["coding"][0]["code"] = "N/A"
condition_template_dict["severity"]["coding"][0]["display"] = "Not Applicable"
condition_template_dict["bodySite"][0]["coding"][0]["system"] = "http://snomed.info/sct"
condition_template_dict["bodySite"][0]["coding"][0]["code"] = "N/A"
condition_template_dict["bodySite"][0]["coding"][0]["display"] = "Not Applicable"
condition_template_dict["bodySite"][0]["text"] = "Not Applicable"
condition_template_dict["onsetDateTime"] = datetime.today().date().isoformat()
condition_template_dict['subject']['reference'] = f"Patient/{patient_resource_id}"
LOADING:
The Loading step involves sending the transformed data to the target system (the Primary Care EHR FHIR server) using HTTP POST requests.
Load Patient Data: The transformed patient data is sent to the FHIR server using a POST request. Load Condition Data: The transformed condition data is sent to the FHIR server using a POST request.
def get_fhir_patient(resource_id):
# Extract and transform patient data (same as above)
...
try:
# Load patient data to Primary Care FHIR server
url = BASE_PRIMARY_CARE_URL + '/' + 'Patient'
response = requests.post(url=url, json=patient_template_dict, headers=headers)
if response.status_code == 200 or response.status_code == 201:
response_data = response.json()
new_patient_resource_id = response_data['id']
with open(data_dir / 'patient_resource_id.txt', 'w') as f:
f.write(new_patient_resource_id)
else:
print('Error')
except Exception as e:
print(e)
def search_condition(patient_resource_id):
# Extract and transform condition data (same as above)
...
try:
# Load condition data to Primary Care FHIR server
url = BASE_PRIMARY_CARE_URL + '/' + 'Condition'
response = requests.post(url=url, json=condition_template_dict, headers=headers)
if response.status_code == 200 or response.status_code == 201:
response_data = response.json()
print(response_data)
except Exception as e:
print(e)
Task 2 - Child Condition: Extraction, Transformation, and Loading Data onto the Target API
Extraction: The extraction step involves retrieving data from the source system. In this case, the source system is an API that provides information on patient conditions (e.g., SNOMED codes related to health conditions). The extraction process also handles API authentication/authorization and error handling.
API Endpoint Details: OpenEMR FHIR Server:
OpenEMR(Source API): “https://in-info-web20.luddy.indianapolis.iu.edu/apis/default/fhir”
SNOMED(Source API):”http://137.184.71.65:8080/fhir”
Primary Care EHR(Target API) “http://137.184.71.65:8080/fhir”
Error handling : While working on this task we need to access the access token which will expire after 1 hr so we need refresh the access token again and have to authorize it . Initially we faced a difficulty in understanding the process later some how we managed to do the process.
Authentication/Authorization:
To authenticate API requests, we retrieve the access token from a file, access_token.json, which contains the credentials required for the request.
def get_access_token_from_file():
file_path = Path(data_dir / "access_token.json")
if not file_path.exists():
print("Error: access_token.json file not found.")
return None
try:
with open(file_path, 'r') as json_file:
json_data = json.load(json_file)
access_token = json_data.get("access_token")
return access_token
except (json.JSONDecodeError, KeyError) as e:
print(f"Error reading access token from file: {e}")
return None
The extraction step refers to retrieving the data from the OpenEMR FHIR server.
Function Involved: search_condition_child(patient_resource_id)
The search_condition_child function sends a GET request to the OpenEMR FHIR server (specified by BASE_URL), querying the conditions associated with a specific patient by using their patient_resource_id. The response from OpenEMR contains a list of conditions associated with the patient. If successful, the SNOMED code of the first condition is extracted.
def search_condition_child(patient_resource_id):
url = f'{BASE_URL}/Condition?patient={patient_resource_id}' # Extracting condition data from OpenEMR
response = requests.get(url=url, headers=get_headers()) # GET request to fetch data
if response.status_code == 200:
data = response.json() # Parsing response data
if 'entry' in data:
conditions = data['entry']
first_condition = conditions[0]
snomed_code_from_openemr = first_condition["resource"]["code"]["coding"][0]["code"]
print(f"Retrieved SNOMED code from the first condition: {snomed_code_from_openemr}")
TRANSFORMATION:
The transformation step involves manipulating and structuring the data to fit the required format for the Primary Care EHR FHIR server. In this case, the SNOMED code retrieved from OpenEMR is used to derive child concept information, and the condition data is transformed into a format suitable for posting to the Primary Care EHR.
Function Involved: Transformation occurs after extracting the SNOMED code from the condition and modifying the data structure for the Primary Care EHR.
The extracted SNOMED code is passed to the constraint_child function to find child concepts, and the child concept details (ID and term) are used to update the condition data. Several other fields in the condition_template_dict are populated with fixed values or values derived from the OpenEMR data.
Tools Used for Transformation:
Python’s JSON Module: For reading and manipulating JSON objects.
Datetime Module: For formatting the current date to match the API’s requirements.
Custom Functions: For resolving SNOMED codes (e.g., constraint_child and expression_constraint).
child_constraint = constraint_child(concept_id=snomed_code_from_openemr) # Transformation: Getting child concept from SNOMED code
child_concept_id, child_concept_term = expression_constraint(search_string=child_constraint) # Transformation: Using child concept for condition data
print(f"Identified Child Concept ID: {child_concept_id}")
print(f"Identified Child Preferred Term: {child_concept_term}")
# Transforming data to fit Primary Care EHR format
condition_template_dict["code"]["text"] = child_concept_term
condition_template_dict["code"]["coding"][0]["display"] = child_concept_term
condition_template_dict["code"]["coding"][0]["code"] = child_concept_id
condition_template_dict['verificationStatus']['coding'][0]['code'] = first_condition['resource']['verificationStatus']['coding'][0]['code']
condition_template_dict["severity"]["coding"][0]["system"] = "http://snomed.info/sct"
condition_template_dict["severity"]["coding"][0]["code"] = "N/A"
condition_template_dict["severity"]["coding"][0]["display"] = "Not Applicable"
condition_template_dict["bodySite"][0]["coding"][0]["system"] = "http://snomed.info/sct"
condition_template_dict["bodySite"][0]["coding"][0]["code"] = "N/A"
condition_template_dict["bodySite"][0]["coding"][0]["display"] = "Not Applicable"
condition_template_dict["bodySite"][0]["text"] = "Not Applicable"
condition_template_dict["onsetDateTime"] = datetime.today().date().isoformat() # Date transformation
primary_care_resource_id = get_patient_resource_id()
condition_template_dict['subject']['reference'] = f"Patient/{primary_care_resource_id}"
Loading:
The loading step involves sending the transformed data to the Primary Care EHR FHIR server.
Function Involved: requests.post inside the search_condition_child function.
After the condition data is transformed, a POST request is sent to the Primary Care EHR system’s /Condition endpoint with the transformed data. If the request is successful (HTTP status 200 or 201), the condition is created in the Primary Care EHR system.
try:
url = f"{BASE_PRIMARY_CARE_URL}/Condition" # Target endpoint for Primary Care EHR
response = requests.post(url=url, json=condition_template_dict, headers=get_headers()) # Sending data to Primary Care EHR
if response.status_code in [200, 201]:
print("New condition with child concept successfully posted to Primary Care EHR.")
print(f"Response Data: {response.json()}")
else:
print(f"Error creating child condition. Status Code: {response.status_code}, Error: {response.text}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Exception during condition creation: {e}")
Task 3 - Observation : Extraction, Transformation, and Loading Data onto the Target API
Extraction: Extract data from an external source, such as a file, API, or database. The get_patient_resource_id function (assumed to be defined in the src.task_1 module) is responsible for fetching a patient resource ID, which is needed to link the observation data to the correct patient.
API Endpoint Details:
BASE_PRIMARY_CARE_URL = “http://137.184.71.65:8080/fhir/Observation”
Error handling : For this task we don’t need to query from OpenEMR so that we didn’t face any problem regrading the access token or authorization we faced very less like indentation errors , basic functional errors we figured it out with out much difficulty.
# Function to get the patient resource ID (assumed to be defined elsewhere)
from src.task_1 import get_patient_resource_id
# Step 1: Read the patient resource ID
patient_resource_id = get_patient_resource_id()
print(f"Patient Resource ID: {patient_resource_id}")
Transformation: Clean and format the data according to the target system’s requirements The create_observation_data function structures the observation data according to the FHIR standard format. This function ensures that the data is organized in the correct format before sending it to the API.
Tools used: Python’s built-in libraries: The tansformation involves creating structured observation data for the FHIR API using Python dictionaries.
def create_observation_data(patient_resource_id):
return {
"resourceType": "Observation",
"meta": {
"versionId": "1",
"lastUpdated": "2024-12-09T17:41:38.679+00:00",
"source": "#ytTzu9ovGo3hKfow",
"profile": ["http://hl7.org/fhir/StructureDefinition/vitalsigns"]
},
"text": {
"status": "generated"
},
"identifier": [{
"system": "urn:ietf:rfc:3986",
"value": "urn:uuid:187e0c12-8dd2-67e2-99b2-bf273c878281"
}],
"basedOn": [{
"identifier": {
"system": "https://acme.org/identifiers",
"value": "1234"
}
}],
"status": "final",
"category": [{
"coding": [{
"system": "http://terminology.hl7.org/CodeSystem/observation-category",
"code": "vital-signs",
"display": "Vital Signs"
}]
}],
"code": {
"coding": [{
"system": "http://loinc.org",
"code": "85354-9",
"display": "Blood pressure panel with all children optional"
}],
"text": "Blood pressure systolic & diastolic"
},
"subject": {
"reference": f"Patient/{patient_resource_id}"
},
"effectiveDateTime": "2012-09-17",
"performer": [{
"reference": "Practitioner/4"
}],
"interpretation": [{
"coding": [{
"system": "http://terminology.hl7.org/CodeSystem/v3-ObservationInterpretation",
"code": "L",
"display": "low"
}],
"text": "Below low normal"
}],
"bodySite": {
"coding": [{
"system": "http://snomed.info/sct",
"code": "368209003",
"display": "Right arm"
}]
},
"component": [{
"code": {
"coding": [{
"system": "http://loinc.org",
"code": "8480-6",
"display": "Systolic blood pressure"
}]
},
"valueQuantity": {
"value": 107,
"unit": "mmHg",
"system": "http://unitsofmeasure.org",
"code": "mm[Hg]"
},
"interpretation": [{
"coding": [{
"system": "http://terminology.hl7.org/CodeSystem/v3-ObservationInterpretation",
"code": "N",
"display": "normal"
}],
"text": "Normal"
}]
}]
}
Loading: Load the transformed data into the target system (e.g., an API, database, or file system). The post_data_to_server function sends the transformed data to the FHIR API using an HTTP POST request. The headers ensure the correct content type is sent, and the data is sent as JSON.
# Function to POST JSON data to an API
def post_data_to_server(observation_data):
headers = {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
}
try:
response = requests.post(BASE_PRIMARY_CARE_URL, json=observation_data, headers=headers)
if response.status_code in [200, 201]:
print("Observation posted successfully!")
print("Response:", response.json())
else:
print(f"Failed to post observation. Status code: {response.status_code}")
print("Error:", response.text)
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e:
print("Error during request:", e)
Task 4 - Procedure : Extraction, Transformation, and Loading Data onto the Target API
EXTRACTION: Extracting data from the API using the requests library in Python. This step involves making HTTP requests to specific endpoints of the FHIR server to retrieve structured healthcare data.
API end point : “http://137.184.71.65:8080/fhir/Procedure”
def post_data_to_server(procedure_data):
headers = {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
}
try:
response = requests.post(BASE_PRIMARY_CARE_URL, json=procedure_data, headers=headers)
if response.status_code in [200, 201]:
print("Procedure posted successfully!")
print("Response:", response.json())
else:
print(f"Failed to post procedure. Status code: {response.status_code}")
print("Error:", response.text)
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e:
print("Error during request:", e)
Error handling : For this task we don’t need to query from OpenEMR so that we didn’t face any problem regrading the access token or authorization we faced very less like indentation errors , basic functional errors we figured it out with out much difficulty.
TRANSFORMATION:
The data is structured in JSON format, following the FHIR Procedure resource specification. The dynamic patient resource ID is inserted into the subject field as a reference. Fixed values like the procedure code and description (“Appendectomy”) are used, as well as the date format for follow-up and notes. The data structure also adheres to the FHIR guidelines for the Procedure resource type.
Tools used to transform
- Python: Used for scripting and data manipulation.
- JSON: Ensures data is in the correct structure for the target API.
- Pathlib: Manages file paths for organized data storage.
- Requests: Handles HTTP requests for data fetching and posting.
- HL7 FHIR Standards: Ensures data complies with healthcare interoperability standards.
def create_procedure_data(patient_resource_id):
return {
"resourceType": "Procedure",
"meta": {
"versionId": "1",
"lastUpdated": "2024-12-09T17:41:39.049+00:00",
"source": "#Obb5mhH5jY5H9V3m"
},
"text": {
"status": "generated"
},
"status": "completed",
"code": {
"coding": [{
"system": "http://snomed.info/sct",
"code": "74400008",
"display": "Appendectomy (Procedure)"
}],
"text": "Appendectomy"
},
"subject": {
"reference": f"Patient/{patient_resource_id}" # Dynamic reference
},
"recorder": {
"reference": "Practitioner/4",
"display": "Dr Adam Careful"
},
"performer": [{
"actor": {
"reference": "Practitioner/4",
"display": "Dr Adam Careful"
}
}],
"followUp": [{
"text": "ROS 5 days - 2024-04-12"
}],
"note": [{
"text": "Routine Appendectomy. Appendix was inflamed and in retro-caecal position"
}]
}
LOADING : The data is sent to the FHIR API using a POST request to the endpoint specified earlier. The requests library is used to send the data, which is in JSON format. After the data is created, the post_data_to_server() function is called to send the data to the FHIR server. The response is checked for success to confirm the successful upload of the procedure data.
# Main execution
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Step 1: Read the patient resource ID
patient_resource_id = get_patient_resource_id()
print(f"Patient Resource ID: {patient_resource_id}")
# Step 2: Create procedure data with the patient resource ID
procedure_data = create_procedure_data(patient_resource_id)
# Step 3: Post the procedure data to the FHIR server
post_data_to_server(procedure_data)
Challenges and Resolutions :
Access Token Expiry: A major challenge was the expiration of the access token after one hour, which interrupted the API interactions with the FHIR servers. To address this, an automated token retrieval file (refresh_token.py) was implemented, ensuring that a valid token is fetched whenever required.
Dynamic Data Mapping: Populating JSON templates with dynamic data, such as SNOMED concepts and patient-specific identifiers, required precise handling to maintain compliance with FHIR standards. This was resolved by carefully debugging the JSON templates and validating the structure against FHIR specifications.
Error Handling in API Requests: Handling failed API requests due to incorrect resource references or missing fields was another issue. Some data fields required by the Primary Care API were not present in the OpenEMR source system. For example, the severity field in our patient’s condition was missing in OpenEMR but mandatory in the Primary Care API. To address this, fallback strategies were implemented, such as using place holders “N/A” to ensure successful data transfer.